#
Virtual Networks
This tutorial explains what is and how to create a Virtual Network in Azure.
The Azure Virtual Network is a logical representation of the network in the cloud. When you need to create a network in Azure, you create an Azure Virtual Network (VNet). When a VNet is defined, we can define our private IP address range for this VNet. On this VNet we can deploy different kinds of Azure resources and different network resources as well.
Communication with the Internet (by default):
- inbound connections not allowed
- outbound traffic allowed
Info
You can communicate inbound to a resource by assigning a public IP address or a public Load Balancer.
The resources such as virtual machines from a VNet are isolated from other resources (from another VNet, etc).
The VNet can be segmented into one or more Subnetworks (Subnets). A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your VNet.
When the subnets are created, the resources are assigned to a specific Subnet.
There are 2 types of Subnets:
public subnet: for resources that need to connect to the Internetprivate subnet: for resources that won't be connected to the Internet
The access of the Subnet resources are protected by Network Security Groups (NSG).
Now, let's create a VNet.
From the Azure Console, go to "All services" -> "Networking" -> "Virtual Networks" and you will see something like this:
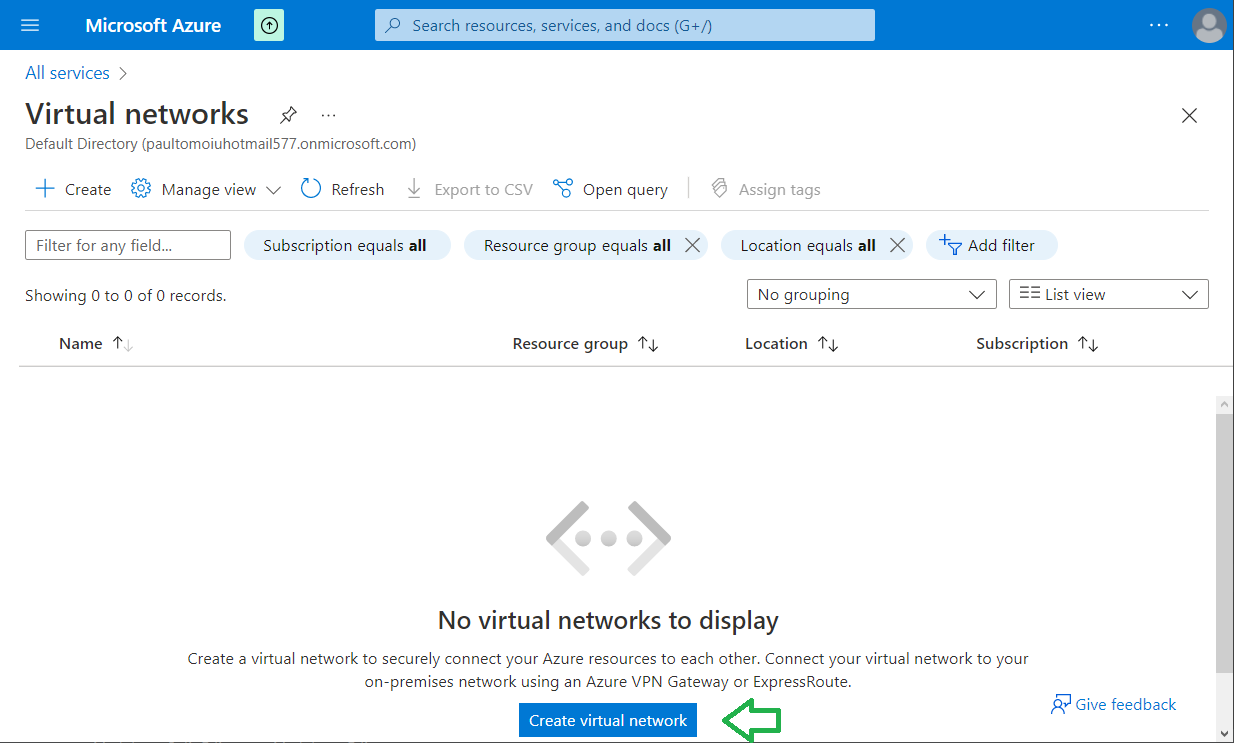
Click on "Create virtual network".
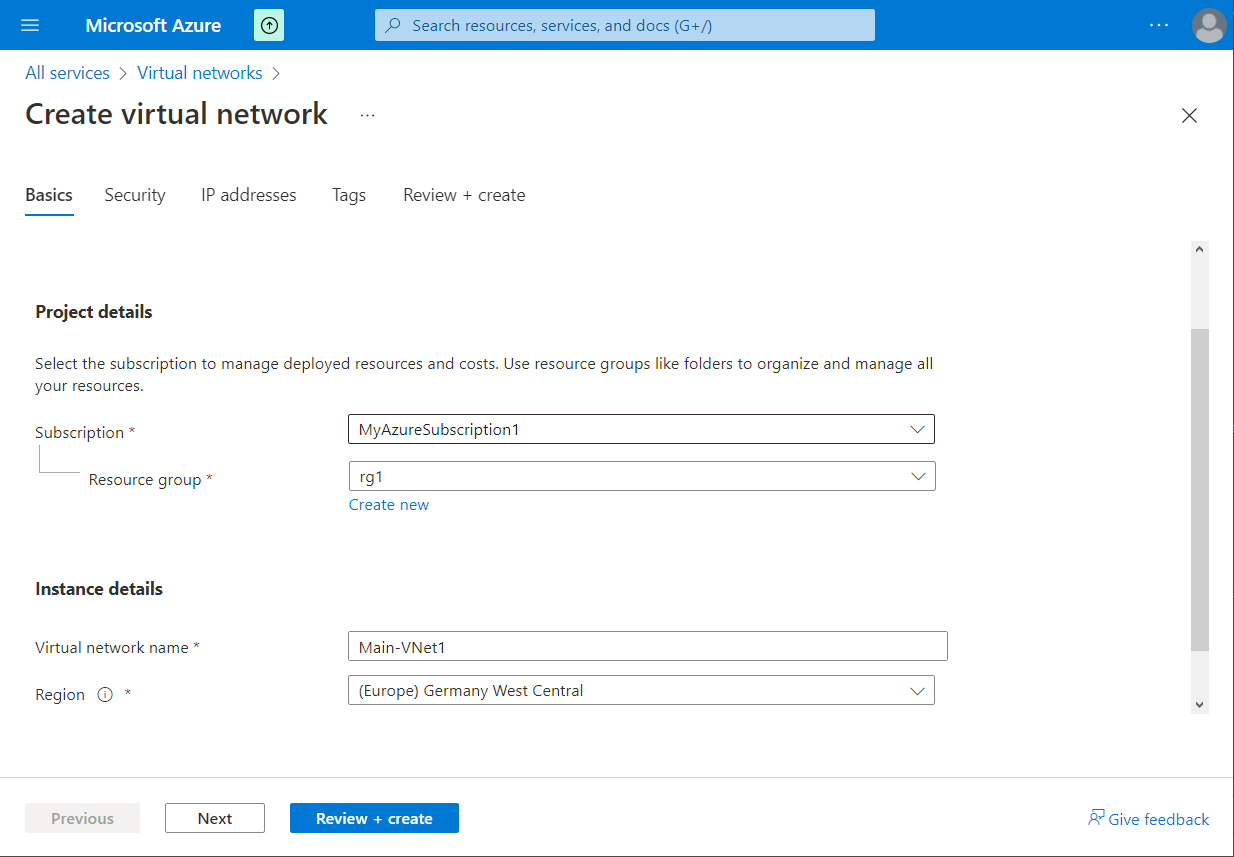
Choose the subscription and the resource group for this VNet, the name of the VNet, the Region where this
resource will be located and click on "Next".
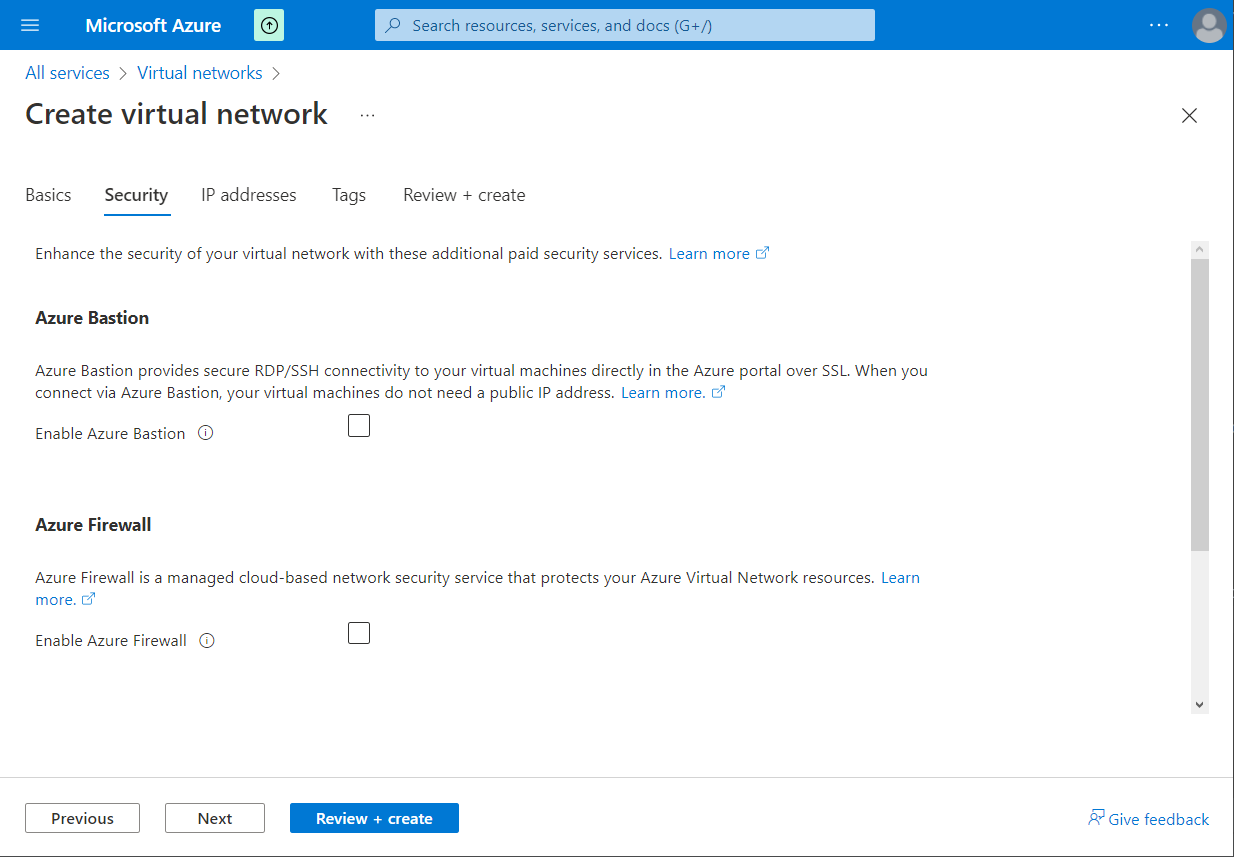
I will not create an Azure Bastion or an Azure Firewall. Click on "Next".
I will create only a VNet without a default subnet. I will not add tags to my VNet, so I can click on "Review + Create" button and after that on "Create".
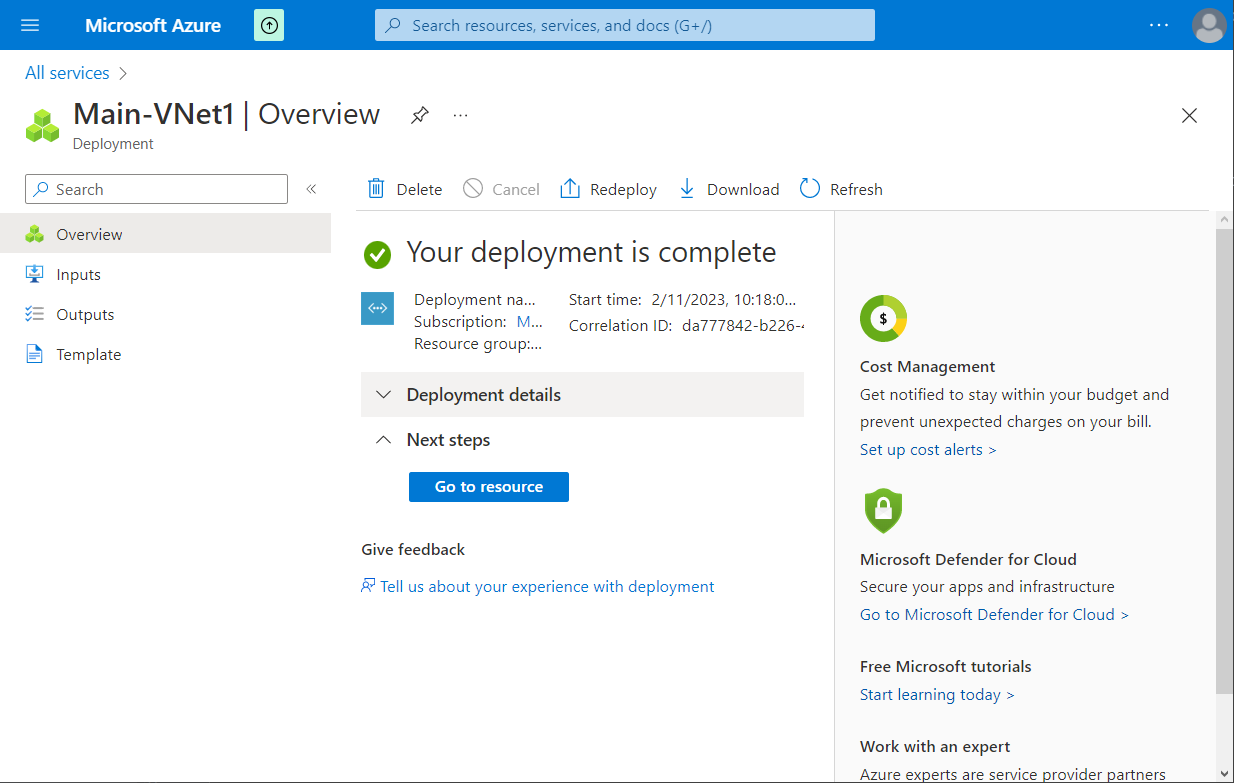
After a while, the VNet will be created: