#
Insert an Entity in a Storage Tables
This tutorial explains how we can insert an entity into a Storage Table in Azure.
Azure Table storage stores large amounts of structured data. The service is a NoSQL datastore which accepts authenticated calls from inside and outside the Azure cloud. Azure tables are ideal for storing structured, non-relational data.
A table is a collection of entities. Tables don't enforce a schema on entities, which means a single table can contain entities that have different sets of properties.
An entity is a set of properties, similar to a database row. An entity in Azure Storage can be up to 1MB in size. An entity in Azure Cosmos DB can be up to 2MB in size.
A property is a name-value pair. Each entity can include up to 252 properties to store data.
Each entity also has three system properties that specify a partition key, a row key, and a timestamp.
Entities with the same partition key can be queried more quickly, and inserted/updated in atomic operations.
An entity's row key is its unique identifier within a partition.
Here is what we have :
a storage account named
storageaccount90011and a table namedMyAzureTable2: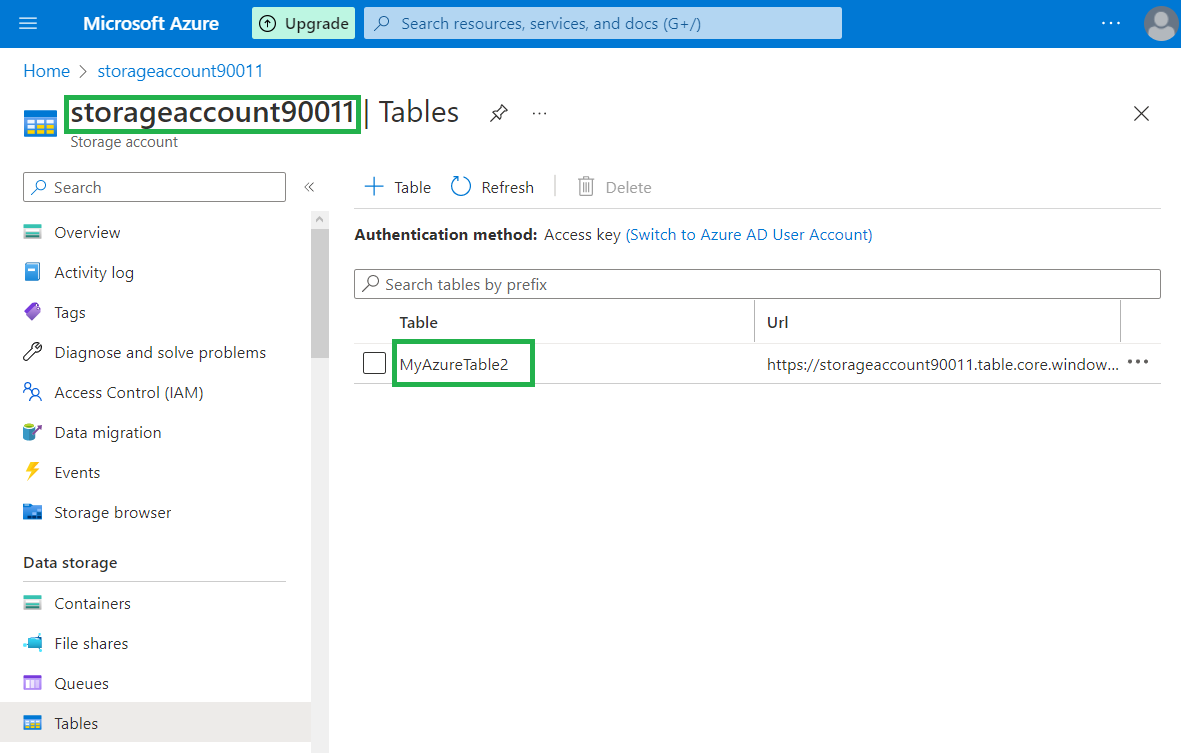
a
Shared Access Signature(SAS) created for the tables in this Storage Account: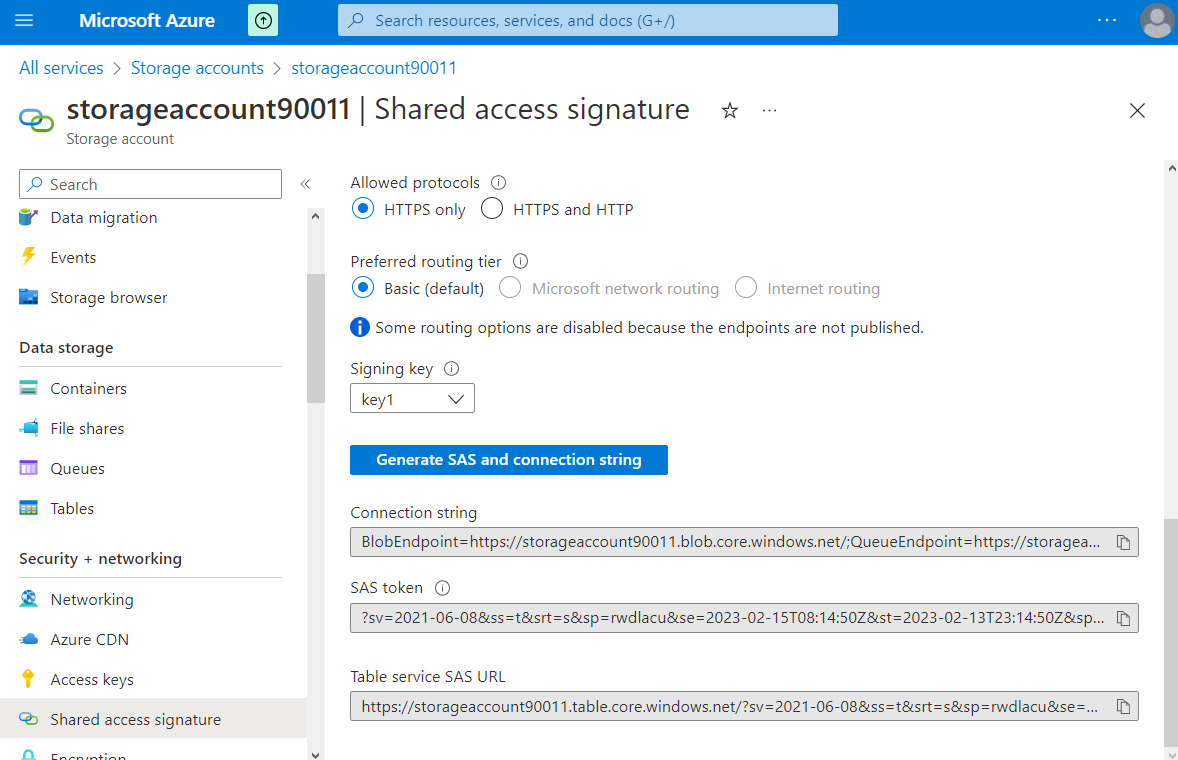
Now we need to insert an entity in the "MyAzureTable2" table from Postman.
Here are the steps:
- Take the Table service SAS URL from a SAS
https://storageaccount90011.table.core.windows.net/?sv=2021-06-08&ss=t&srt=s&sp=rwdlacu&se=2023-02-15T08:14:50Z&st=2023-02-13T23:14:50Z&spr=https&sig=ewX7nzKPlKOj7t8n%2BQEb4jerlprU5uXXy6BInEJ%2Bb5M%3D- Add the table name in Table service SAS URL The table name must be added between "/" and "?" signs, and we will obtain:
https://storageaccount90011.table.core.windows.net/MyAzureTable2?sv=2021-06-08&ss=t&srt=s&sp=rwdlacu&se=2023-02-15T08:14:50Z&st=2023-02-13T23:14:50Z&spr=https&sig=ewX7nzKPlKOj7t8n%2BQEb4jerlprU5uXXy6BInEJ%2Bb5M%3DCopy in Postman the command above
Prepare the workload to be sent to the Azure table
Here is the body of the request:
{
"PartitionKey":"mypartitionkey1",
"RowKey":"myrowkey1",
"Order":"DF5554545454",
"Location":"South Lake"
}- Run the request as a POST request
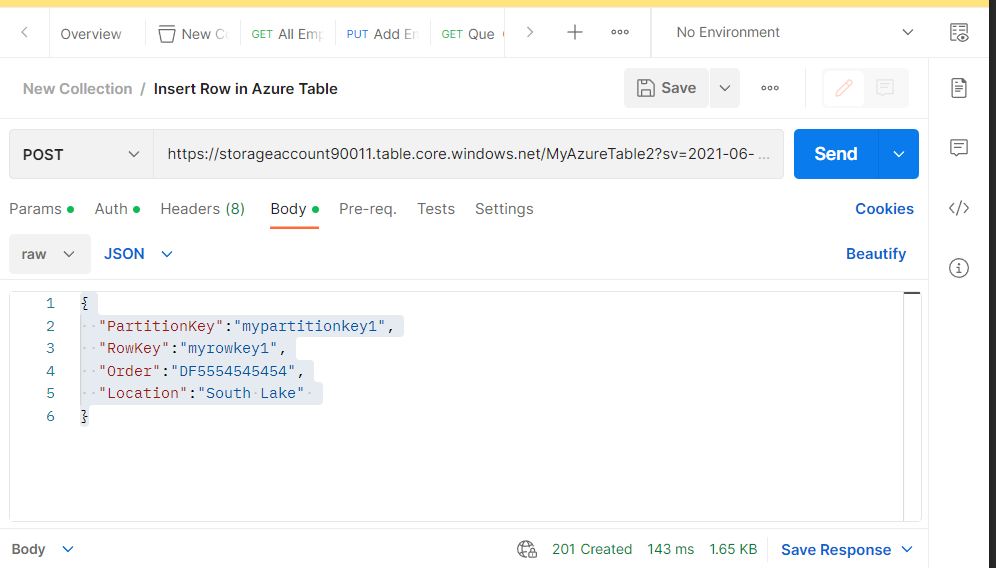
And you will receive a response body like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<entry xml:base="https://storageaccount90011.table.core.windows.net/" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ado/2007/08/dataservices" xmlns:m="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ado/2007/08/dataservices/metadata" xmlns:georss="http://www.georss.org/georss" xmlns:gml="http://www.opengis.net/gml" m:etag="W/"datetime'2023-02-14T13%3A18%3A15.9990469Z'"">
<id>https://storageaccount90011.table.core.windows.net/MyAzureTable2(PartitionKey='mypartitionkey1',RowKey='myrowkey1')</id>
<category term="storageaccount90011.MyAzureTable2" scheme="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ado/2007/08/dataservices/scheme" />
<link rel="edit" title="MyAzureTable2" href="MyAzureTable2(PartitionKey='mypartitionkey1',RowKey='myrowkey1')" />
<title />
<updated>2023-02-14T13:18:16Z</updated>
<author>
<name />
</author>
<content type="application/xml">
<m:properties>
<d:PartitionKey>mypartitionkey1</d:PartitionKey>
<d:RowKey>myrowkey1</d:RowKey>
<d:Timestamp m:type="Edm.DateTime">2023-02-18T13:18:15.9990469Z</d:Timestamp>
<d:Order>DF5554545454</d:Order>
<d:Location>South Lake</d:Location>
</m:properties>
</content>
</entry>
