#
IPs, Hostnames, Ports in Docker Containers
This tutorial explains some concepts regarding IPs, hostnames, ports in Docker containers.
Here are some important things to know :
A container has no information about what kind of network it’s attached to (a bridge, an overlay, a macvlan network, or a custom network plugin). A container only sees a network interface with an IP address, a gateway, a routing table, DNS services, and other networking details (excepting containers which use the
nonenetwork driver where there are no such information).By default, when you create or run a container using
docker createordocker run, the container doesn’t expose any of it's ports to the outside world. To make a port available to services outside of Docker, or to Docker containers running on a different network, use the--publishor-pflag.
Examples:
By default, the container gets an IP address for every Docker network it attaches to (excepting containers which use the
nonenetwork driver). The Docker daemon effectively acts as a DHCP server for each container.When a container starts, it can only attach to a single network, using the
--networkflag. You can connect a running container to multiple networks using thedocker network connectcommand.When you use the
--networkflag, you can specify the IP address for the container on that network using the--ipor--ip6flags.You can override the hostname using
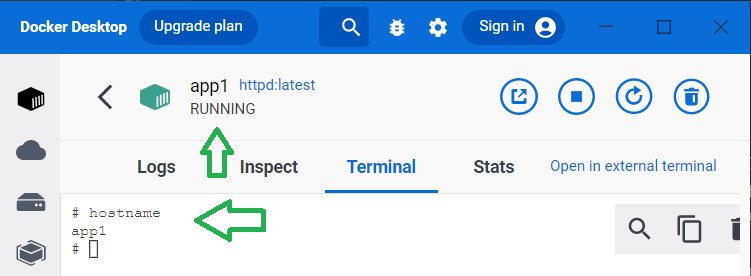
--hostname.
For instance, you can run the following command:
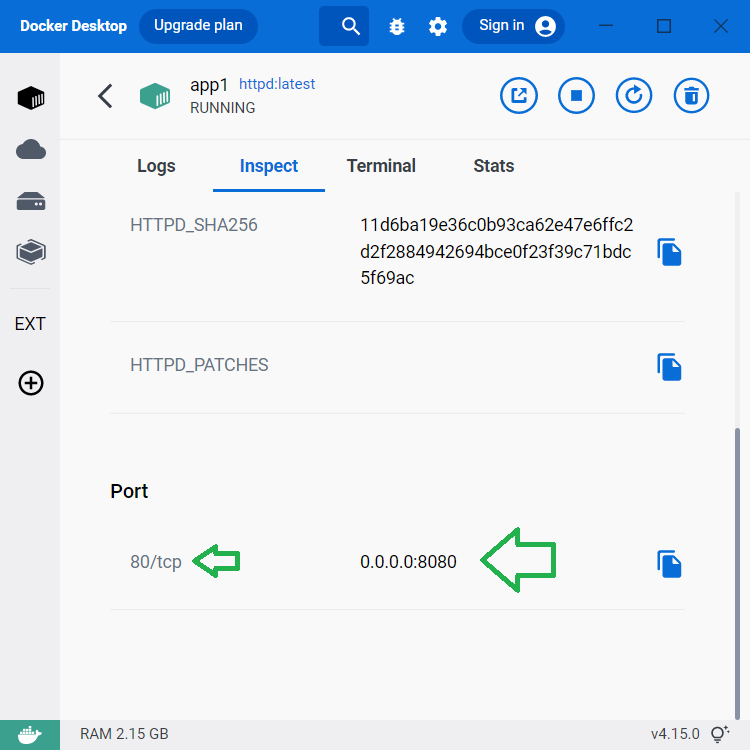
docker run -d --name app1 -p 8080:80 --hostname app1 httpd:latestYou will see that an app1 container is created, and its hostname is app1.
The container use the port 80 which is mapped to Docker's port 8080.