#
Logback : Configuration for Java
This tutorial explains to you how to configure the Logback for Java. This tutorial is using Eclipse and Maven. This is for a simple Java application.
Logback is a generic, reliable, fast and flexible logging library for Java.
Here is the architecture overview of Logback framework:
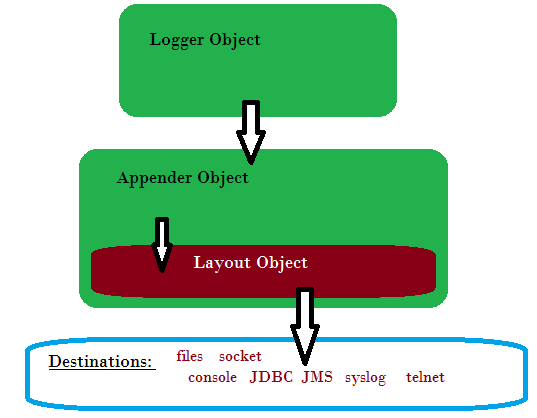
Here are some good things to know regarding the Logback architecture:
- The
Logback Loggerobject is responsible for capturing logging information - Each Logger is independently configurable
- A Logger can send log messages to multiple Appenders
- The
Logback Layoutobject is used to format logging information (we can get "one-line-at-a-time", XML, HTML, JSON and other formats) - The
Logback Appenderobject is responsible for writing (publishing) logging information to various destinations such as a files, databases, JMS, console, UNIX Syslog, etc.
Here are the steps for configuring an existing Maven Java application for using log4j:
- Add the following in pom.xml :
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ch.qos.logback/logback-classic -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>You can take a look to the following picture as well:
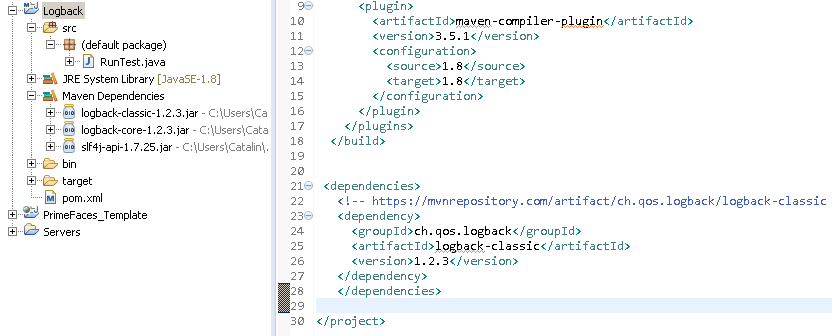
Info
As you can see into the picture above, Maven take all the dependencies it needs. Even if I put "logback-classic" in pom.xml, Maven download "logback-core" and "slf4j-api" as well.
Build the project using Maven in order to obtain the Logback libraries.
Create a directory "resources" (for instance) under src folder
Create the logback.xml file in it.
Here is the logback.xml content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<property name="LOG_DIR" value="C:/JAVA" />
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} | %-5p | [%thread] %logger{5}:%L - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.FileAppender">
<file>${LOG_DIR}/logFile.log</file>
<append>true</append>
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} | %-5p | [%thread] %logger{5}:%L - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="myLogger" level="TRACE"/>
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
</root>
</configuration>When you run your project, configure the CLASSPATH and add the location of the logback.xml files by clicking on:
Run As ->Run Configuration -> Classpath tab -> click on User Entries -> Advanced -> select Add Folder -> select the location of your logback.xml file and then -> OK -> Run.
Now you can use Logback framework using a basic configuration.
Info
Logback can be configured either programmatically or with a configuration script expressed in XML or Groovy format.
Logback tries to find a file called logback.groovy in the classpath. If this is not found it tries for the following files (in this order): logback-test.xml, logback.xml.
If no configuration file is found, logback configures itself automatically using the BasicConfigurator which will cause logging output to be directed to the console. For this reason if something is wrong into the configuration of Logback, you will see the messages only into the console.

