#
Create a REST Server
Spring Boot is designed to speed up the development of Spring applications by writing less boilerplate code. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run". Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration.
In this tutorial I will create a Spring Boot REST Web Service Server.
First of all, you need to create a simple Spring Application configured with Maven.
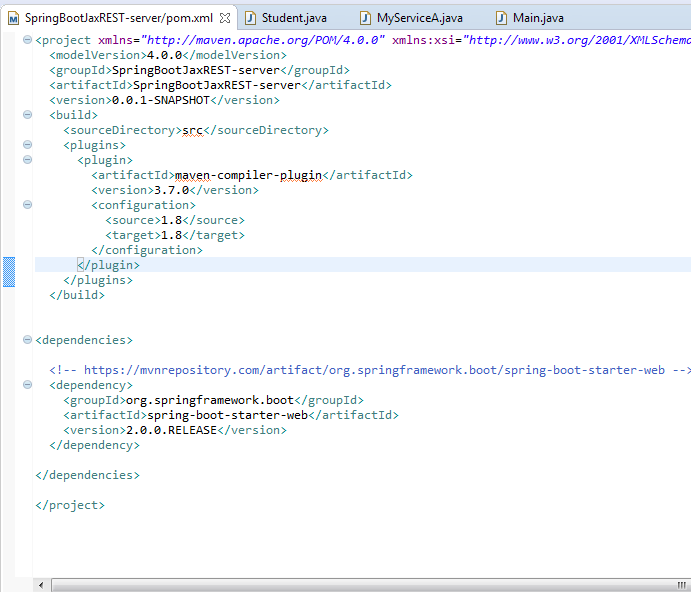
After that you need to configure Maven using pom.xml file . Here is the POM configuration for a simple
Spring Boot REST Web Service Server:
After that you have to add the following classes to the Spring Boot REST Web Service Application :
package com.example.ws;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}package com.example.main;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.ws.Student;
@RestController
public class MyServiceA {
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(@RequestParam("value1") int value1,
@RequestParam("value2") int value2) {
int theSum = value1+value2;
return "The SUM is ="+theSum+".";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/student/{name}/{age}",
produces={ "application/json", "application/xml" })
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable("name") String name,
@PathVariable("age") int age) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setAge(age);
student.setName(name);
return student;
}
}package com.example.main;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
System.out.println("Start application ...");
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
}Info
@SpringBootApplication annotation is a shortcut for the following annotation: @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, @ComponentScan
the scanning for Beans in done only in the current package and all its subpackages
Spring Boot Autoconfiguration creates and configure Context Beans automatically based on the dependencies we have chosen
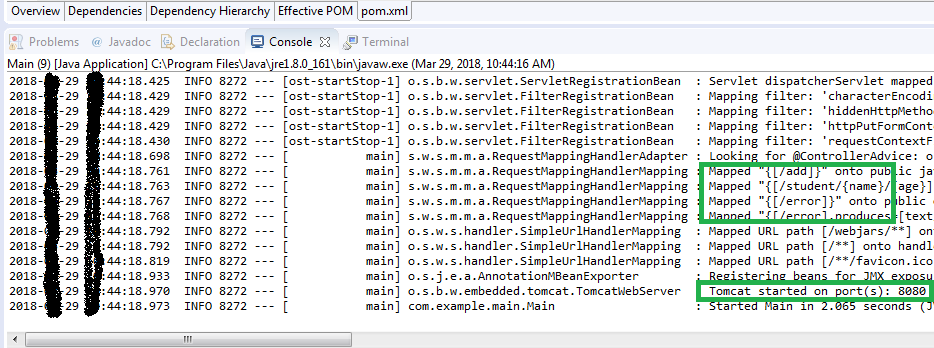
When we run the Spring Boot REST Web Service Application we receive the following output: