#
Spring Data JPA : Transactions - example
This tutorial explains how we can define transactions in a Spring Data JPA application. This example uses a MySql database.
#
Install the MySql database
In my case I will install MySql database as a Docker container. In my case I am using Docker Desktop.
You need to run the docker pull mysql command in order to get the MySql image from docker.io.
C:\Users\Catalin>docker pull mysql
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from library/mysql
e2c03c89dcad: Pull complete
68eb43837bf8: Pull complete
796892ddf5ac: Pull complete
6bca45eb31e1: Pull complete
ebb53bc0dcca: Pull complete
2e2c6bdc7a40: Pull complete
6f27b5c76970: Pull complete
438533a24810: Pull complete
e5bdf19985e0: Pull complete
667fa148337b: Pull complete
5baa702110e4: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:232936eb036d444045da2b87a90d48241c60b68b376caf509051cb6cffea6fdc
Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest
docker.io/library/mysql:latestYou need to run the docker run --name my-mysql -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=p -d mysql command in order to create the mysql
container containing a MyQql instance in it. The container port 3306 will be exposed on the host side with the same port number.
C:\Users\Catalin>docker run --name my-mysql -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=p -d mysql
74d074e24c50bba5ced5e52c0cfab1006903d87be36a406fe1e1f075efe450f7For this example, I installed a trial version of DataGrip (MySql admin client).
With this admin tool I create a MySql database schema named "mydb" and a table "employees" as in the picture below:
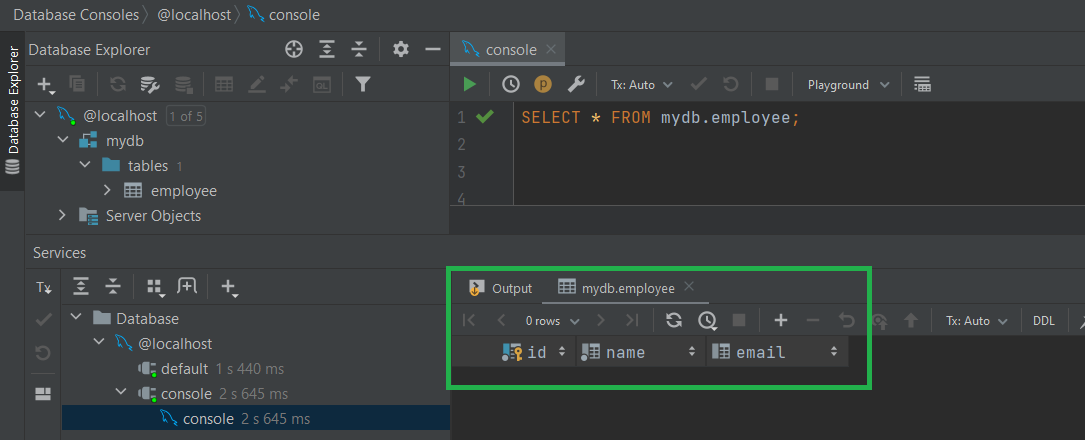
Here is the code for creating the table:
create table employee
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
name text not null,
email text null
);
#
Create the Spring Boot application
Now, let's create the Spring Boot application using Spring Data JPA.
First of all I will create a simple Spring Boot application using spring initializr
as in the image below:
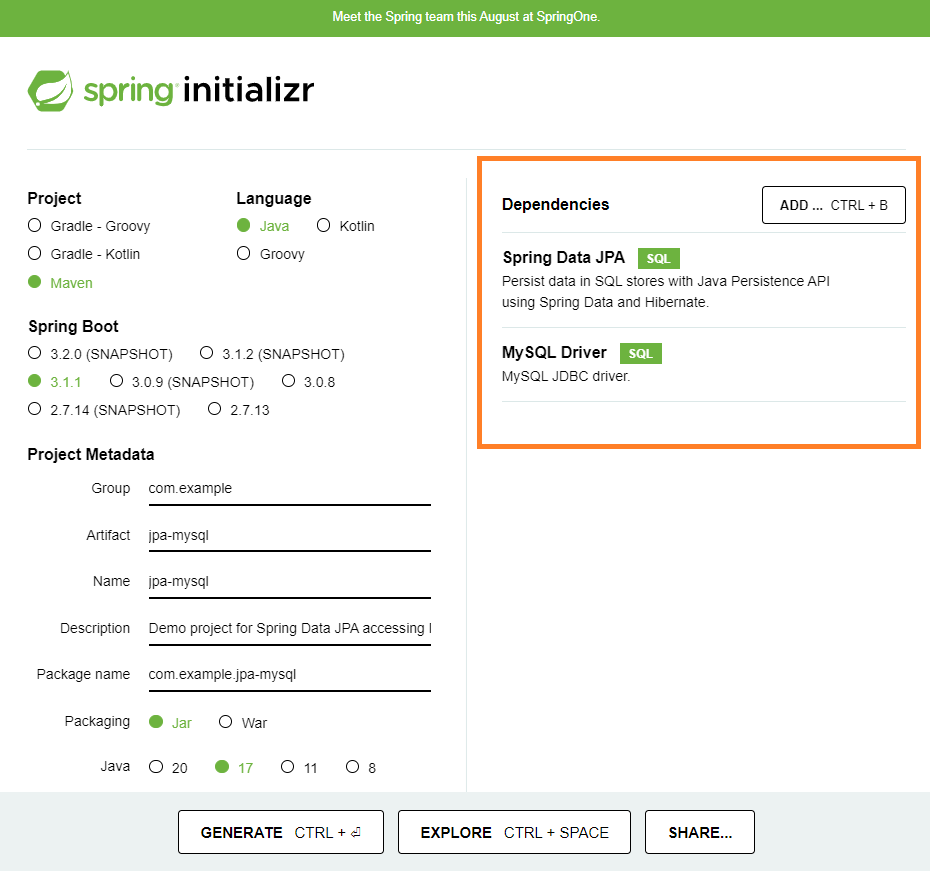
In pom.xml we can see the following dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>Now we can create an entity class:
package com.example.jpamysql.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Employee {
public Employee() { }
public Employee(int id, String name, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
String name;
String email;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}Info
- The entity class must have
@Idannotation for underlying the column in the database which is the primary key. - We mark also the class with
@Entityannotation for telling that this is an entity in a database. - This class must have a default constructor.
Now, let's configure the DataSource:
package com.example.jpamysql;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
@Configuration
public class ConfigApp {
@Bean
public DriverManagerDataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("p");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb");
return dataSource;
}
}Now let's configure the EmployeeRepository interface. This interface is specific to Spring Data.
When we configure this interface, the needed classes/methods are autogenerated.
package com.example.jpamysql.interfaces;
import com.example.jpamysql.entity.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query(value = "INSERT INTO employee VALUES " +
"( :#{#emp.id}, :#{#emp.name}, :#{#emp.email} )", nativeQuery = true)
public abstract void myInsertOk(@Param("emp") Employee emp);
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query(value = "INSERT INTO employee_table VALUES " +
"( :#{#emp.id}, :#{#emp.name}, :#{#emp.email} )", nativeQuery = true)
public abstract void myInsertNok(@Param("emp") Employee emp);
}Info
The @Modifying annotation is used to let the @Query annotation to allow INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and even DDL queries
in addition to SELECT queries.
Let's create a DAO class/object:
package com.example.jpamysql.dao;
import com.example.jpamysql.entity.Employee;
import com.example.jpamysql.interfaces.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired
EmployeeRepository eRepository;
// This is not into a transaction
public void eraseAll(){
eRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Transactional(propagation= Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation= Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)
public void insert2EmpOk() {
Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Dan", "dan@k.com");
Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Anna", "anna@k.com");
// The "save" method is auto-generated, and it is not defined by me
eRepository.save(emp1);
// The "myInsert" method is auto-generated and defined by me
eRepository.myInsertOk(emp2);
}
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation=Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)
public void insert2EmpNok() {
Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Dan", "dan@k.com");
Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Anna", "anna@k.com");
// The "save" method is auto-generated, and it is not defined by me
eRepository.save(emp1);
// The "myInsert" method is auto-generated and defined by me
eRepository.myInsertNok(emp2);
}
}And here we have the main class of the application:
package com.example.jpamysql;
import com.example.jpamysql.dao.EmployeeDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class JpaMysqlApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(JpaMysqlApplication.class, args);
EmployeeDao employeeDao = context.getBean(EmployeeDao.class);
employeeDao.eraseAll();
employeeDao.insert2EmpOk();
employeeDao.insert2EmpNok();
}
}Info
- Please take a look at the comment above in order to understand how Spring Data is working.
EmployeeRepositorycould extendsCrudRepository,PagingAndSortingRepositoryorJpaRepository. CrudRepository defines the CRUD methods. PagingAndSortingRepository defines methods for pagination and sorting (extends CrudRepository). JpaRepository provides some JPA-related methods such as flushing the persistence context and deleting records in a batch (extends CrudRepository and PagingAndSortingRepository).
Test case #1
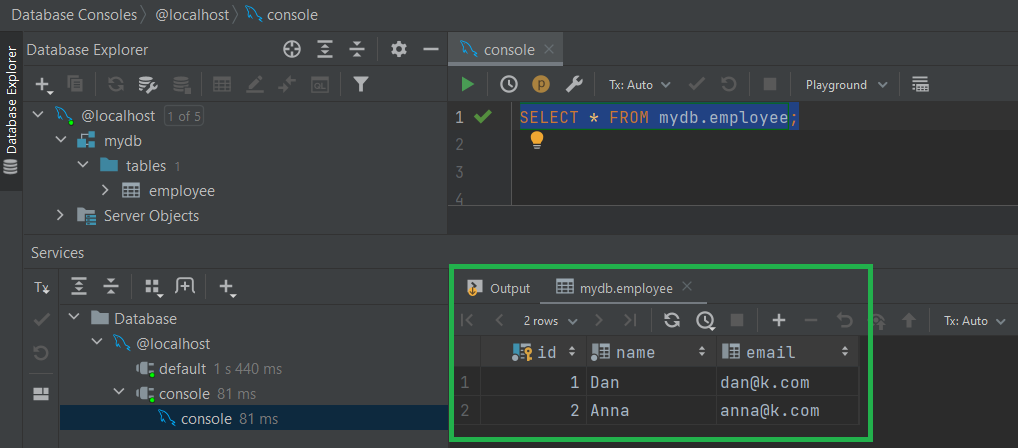
We comment employeeDao.insert2EmpNok(); in the main class and run the application.
Result:
In the database we can see all the inserted rows:
Test case #2
We comment employeeDao.insert2EmpOk(); in the main class and run the application.
Result: There are no rows inserted in the database and in the console we can see the following error:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.dao.InvalidDataAccessResourceUsageException: JDBC exception executing SQL [INSERT INTO employee_table VALUES ( ?, ?, ? )] [Table 'mydb.employee_table' doesn't exist] [n/a]; SQL [n/a]
at org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect.convertHibernateAccessException(HibernateJpaDialect.java:256)
at org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect.translateExceptionIfPossible(HibernateJpaDialect.java:229)So, as we can se the insert statements are done together or not at all.
Info
For handling the transactions, Spring generates a proxy object that wraps the method which is a part of the transaction
and provides the required code to manage the transaction.
Info
For handling the creation of new transactions or working with the existing ones we use some propagation settings:
REQUIRED: tells Spring to either join an active transaction or to start a new one if the method gets called without a transaction. This is the default behavior.SUPPORTS: joins an activate transaction if one exists. If the method gets called without an active transaction, this method will be executed without a transactional context.NOT_SUPPORTED: suspends an active transaction and to execute the method without any transactional context.REQUIRES_NEW: always starts a new transaction for this method. If the method gets called with an active transaction, that transaction gets suspended until this method got executed.NESTED: starts a new transaction if the method gets called without an active transaction. If it gets called with an active transaction, Spring sets a savepoint and rolls back to that savepoint if an Exception occurs.MANDATORY: joins an activate transaction if one exists or to throw an Exception if the method gets called without an active transaction.NEVER: throws an Exception if the method gets called in the context of an active transaction.
Info
There are some ways we can perform transactions using isolation property:
READ_UNCOMMITTED: Allows dirty reads.READ_COMMITTED: Does not allow dirty reads.REPEATABLE_READ: If a row is read twice in the same transaction, the result will always be the same.SERIALIZABLE: Performs all transactions in a sequence. This is the highest isolation level.

