#
Spring Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Server example
This tutorial explains to you how to create a Spring Remote Method Invocation (RMI) server and also provides you with an example.
RMI stands for Remote Method Invocation. It is a mechanism that allows an object residing in one Java container
to access/invoke an object running on another Java container (generally on another host, but not necessarily).
The Object instances are serialized and send over the network.
In order to access the remote object, the RMI server must declare an exporter and the client a proxy.
In this tutorial you will have an example of using Remote Method Invocation (RMI) in Spring.
For creating the example, you have to create a simple Maven & Spring project.
Here you have the dependencies you need in the pom.xml file:
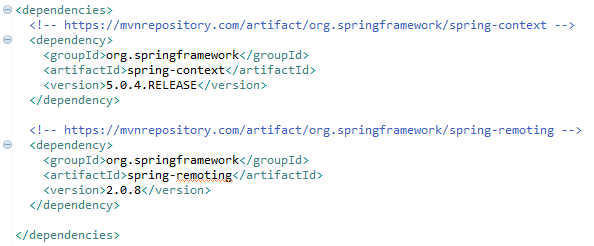
Now you have to add the following classes to your projects:
package com.example.interfaces;
public interface IMyServiceA {
public String addNumbers(int val1, int val2);
}package com.example.services;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.interfaces.IMyServiceA;
@Service
public class MyServiceA implements IMyServiceA {
@Override
public String addNumbers(int val1, int val2) {
int sum = val1 + val2;
return "The SUM is "+sum;
}
}package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiServiceExporter;
import com.example.interfaces.IMyServiceA;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example.*")
public class SpringContextConfig {
@Bean
@Autowired
public RmiServiceExporter rmiServiceExporter (IMyServiceA service) {
RmiServiceExporter exporter = new RmiServiceExporter();
exporter.setServiceName("ServiceA");
exporter.setService(service);
exporter.setServiceInterface(IMyServiceA.class);
//exporter.setRegistryHost("localhost");
exporter.setRegistryPort(4400);
return exporter;
}
}package com.example.main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.example.config.SpringContextConfig;
public class Main {
public static void main(String [] arg) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringContextConfig.class);
}
}When you run the project you will see the following log:
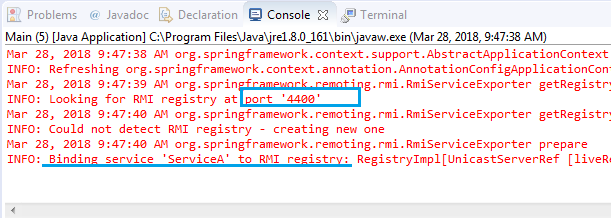
Info
- The RMI is used generally inside the same company because it is harder to maintain than a Web Service;
- A Web Service is using HTTP protocol, and it is slower than RMI;
- Consuming a Web Service is generally easier than a service exported via RMI.

