#
Spring Context Configuration using with XML file
This tutorial explains to you how Spring Context Configuration is done using one XML file. This tutorial has an example as well.
Spring context is a Spring container which is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling beans by reading configuration metadata from XML files, Java annotations or both.
In order to create and configure a Spring context using a XML file you have to create a Maven Spring project.
Here it is the Maven pom.xml file dependencies:
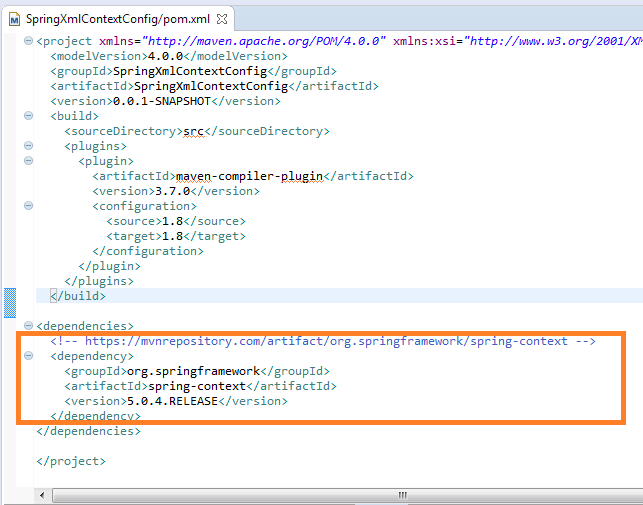
After that you have to create the following XML configuration file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="carCurrentSpeed" class="com.example.beans.CurrentSpeed">
<constructor-arg name="speed" value="100" />
</bean>
</beans>Add the following classes:
package com.example.main;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import com.example.beans.CurrentSpeed;
public class Main {
public static void main (String [] args) {
System.out.println("Start Java Application ...");
//The Spring context is configured from a Java Class for a Java Application
// (Not for a Web Application)
// FileSystemXmlApplicationContext --> used when the context is defined in an xml file.
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context
= new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\\Java\\SPRING\\workspace\\SpringXmlContextConfig\\src\\com\\example\\config\\myContextConfig.xml");
System.out.println("Spring context created ...");
//GET an instance from context BY CLASS
// SINGLETON by default in Spring
CurrentSpeed cSpeed = context.getBean(CurrentSpeed.class);
System.out.println("Current speed = "+cSpeed.getSpeed());
//Change the speed for the context bean
cSpeed.setSpeed(20);
CurrentSpeed cSpeed2 = context.getBean(CurrentSpeed.class);
System.out.println("Current speed = "+cSpeed2.getSpeed());
//GET an instance from context BY NAME
CurrentSpeed cSpeed3 = context.getBean("carCurrentSpeed", CurrentSpeed.class);
System.out.println("Current speed = "+cSpeed3.getSpeed());
context.close();
}
}package com.example.beans;
public class CurrentSpeed {
private int speed;
public CurrentSpeed() {
this.speed = 0;
}
public CurrentSpeed(int speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
public int getSpeed() {
return this.speed;
}
public void setSpeed(int cSpeed) {
this.speed = cSpeed;
}
}When you run the code you will se the following result :