#
Store Users & Passwords into a MySql database
This tutorial explains to you how we can define users with passwords and keep this information into a MySql database.
This tutorial starts from the result of the tutorial Disable the CSRF.
#
Create a MySql database
For this example, I created a free MySql database on FreeMySqlHosting.net. After the database creation, I receive the database name and the credentials in an email.
What I have received is :
Server: sql7.freemysqlhosting.net
Name: sql7628853
Username: sql7628853
Password: e91IgdmvwVw1
Port number: 3306
#
Configure Spring Boot in order to connect to MySql database
All we need is to:
- add the following lines in the application.properties file
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://sql7.freemysqlhosting.net:3306/sql7628853
spring.datasource.username=sql7628853
spring.datasource.password=e91IgdmvwVw1
spring.sql.init.mode:always
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver- add the following dependencies in pom.xml:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.mysql/mysql-connector-j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
#
Define the USERS & AUTHORITIES tables
All the DDL commands will be written in "src/main/resources/schema.sql" file.
Here we have the content of schema.sql file:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sql7629253`.`users` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,
`username` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
`password` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
`active` INT NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE = InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sql7629253`.`authorities` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,
`username` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
`authority` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE = InnoDB;Info
The name and the location of the files ("schema.sql","data.sql") are fixed. We don't need to modify these names.
#
Insert data into USERS & AUTHORITIES tables
All the INSERT commands will be written in "src/main/resources/data.sql" file.
Here we have the content of data.sql file:
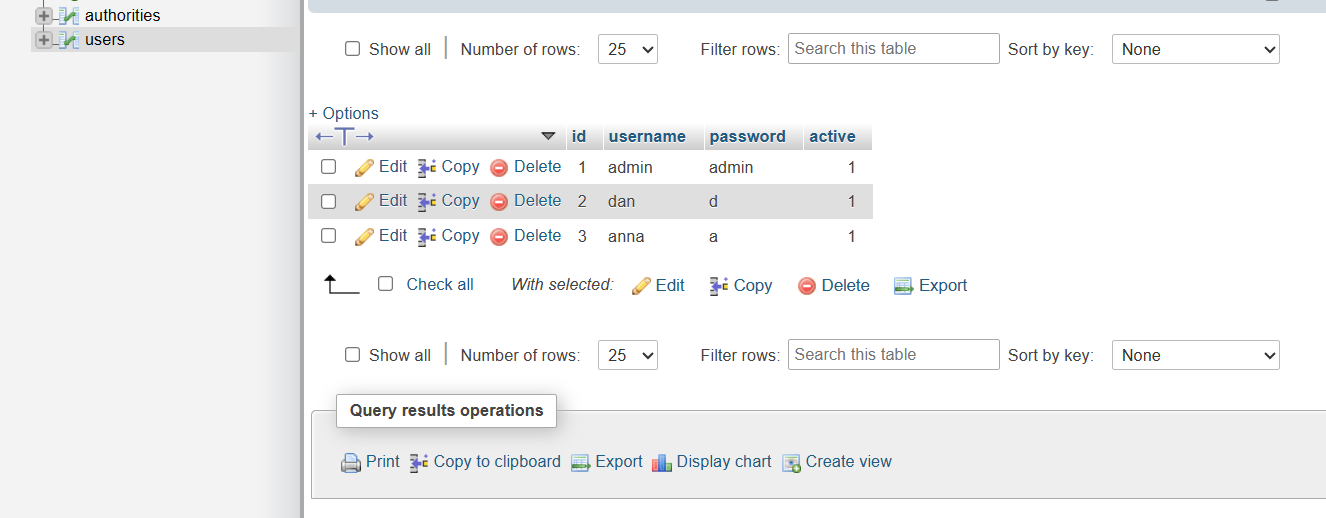
INSERT IGNORE INTO `users` values (NULL, 'admin', 'admin', '1');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `users` values (NULL, 'dan', 'd', '1');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `users` values (NULL, 'anna', 'a', '1');
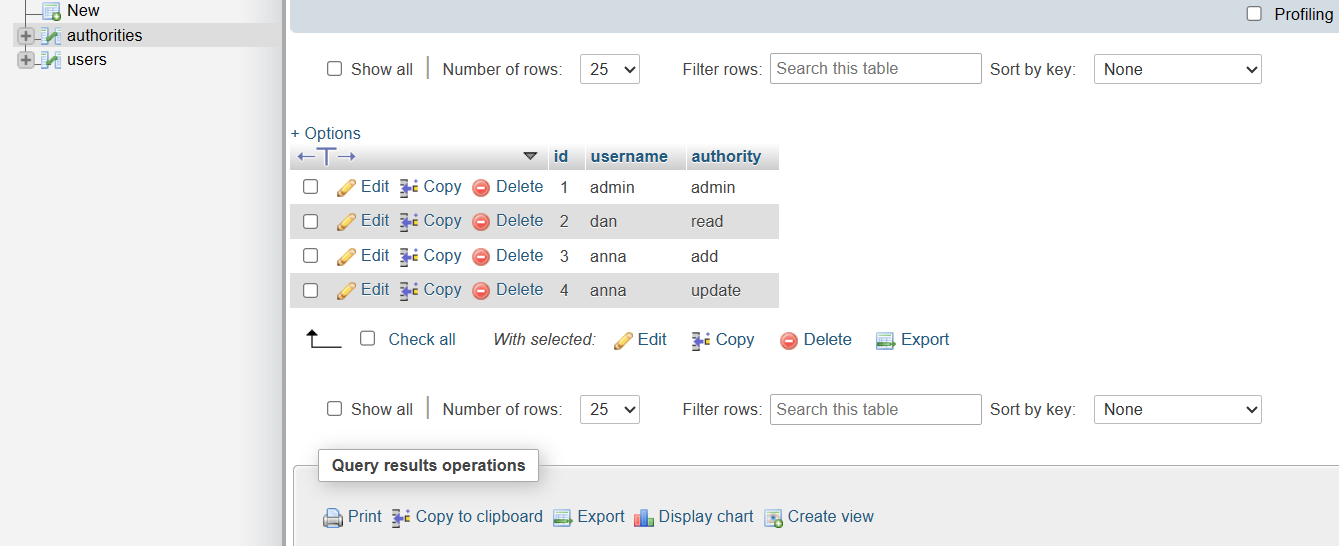
INSERT IGNORE INTO `authorities` values (NULL, 'admin', 'admin');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `authorities` values (NULL, 'dan', 'read');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `authorities` values (NULL, 'anna', 'add');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `authorities` values (NULL, 'anna', 'update');
#
See the result
When we start the application the commands found in "schema.sql","data.sql" will be run against the MySql database.
In MySql Database we will see something like this:
If we want we can change the tables and the columns names, for being recognized by Spring Boot Security, but this is another topic. The names I have used in this article are recognized by default.

