#
SPRING Security : Simple MVC Application (no security)
This tutorial explains to you how you can create a simple Spring simple mvc application with no security enforcement. This application will be used to explain later the main concepts of Spring Security.
In order to secure a Web MVC application with Spring Security 5, you need to have a unsecured application. In this tutorial I will create a unsecured application created using Spring 5 and after that I will secure it.
In my case I use Spring Tool Suite and at the beginning I will create a simple web Maven application.
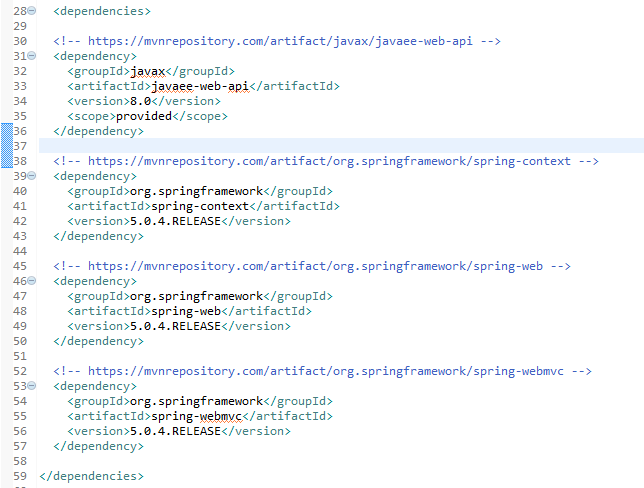
I will have the following dependencies in pom.xml file:
and I create the following application folders and files:
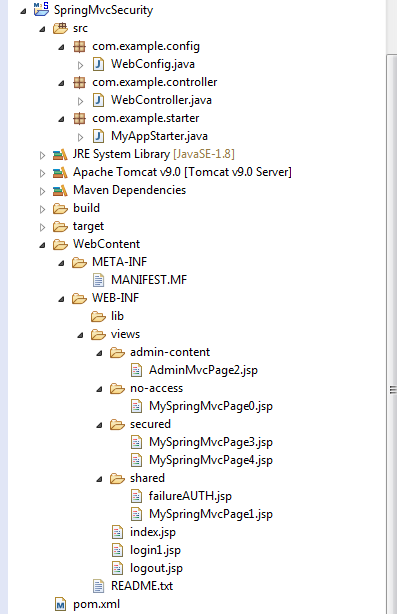
... and here are the content of the following files (in this order) WebConfig.java, WebController.java, MyAppStarter.java (login & logout pages and README.txt are not important for this example):
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewResolverRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages= {"com.example.controller"})
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.jsp().prefix("/WEB-INF/views/").suffix(".jsp");
}
}package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewResolverRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages= {"com.example.controller"})
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.jsp().prefix("/WEB-INF/views/").suffix(".jsp");
}
}package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class WebController {
@GetMapping(value="/")
public String index(ModelMap model) {
// Anytime you can read variables from Spring context
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/shared/MySpringMvcPage1", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String mySpringMvcPage1(Model m) {
return "/shared/MySpringMvcPage1";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/secured/MySpringMvcPage3", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String mySpringMvcPage3(Model m) {
return "/secured/MySpringMvcPage3";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/secured/MySpringMvcPage4", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String mySpringMvcPage4(Model m) {
return "/secured/MySpringMvcPage4";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/login1", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String mySpringMvcLogin(Model m) {
System.out.println("Login - controller ...");
return "/login1";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/no-access/MySpringMvcPage0", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String mySpringMvcPage0(Model m) {
return "/no-access/MySpringMvcPage0";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/shared/failureAUTH", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String failureAUTH() {
return "/shared/failureAUTH";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/admin-content/AdminMvcPage2", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String adminMcvPage1() {
return "/admin-content/AdminMvcPage2";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/logout", method=RequestMethod.GET)
//Anytime you can use @RequestParam and @PathParam in order to read the
//parameters you have received
public String logout() {
return "/logout";
}
}package com.example.starter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import com.example.config.WebConfig;
public class MyAppStarter extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer{
@Override
protected Class<!--?-->[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {};
}
// Load spring web configuration
@Override
protected Class<!--?-->[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {WebConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] {"/"};
}
}Here are the AdminMvcPage2.jsp, MySpringMvcPage0.jsp, MySpringMvcPage3.jsp, MySpringMvcPage4.jsp, MySpringMvcPage1.jsp, index.jsp, failureAUTH.jsp, login1.jsp, logout.jsp (in this order):
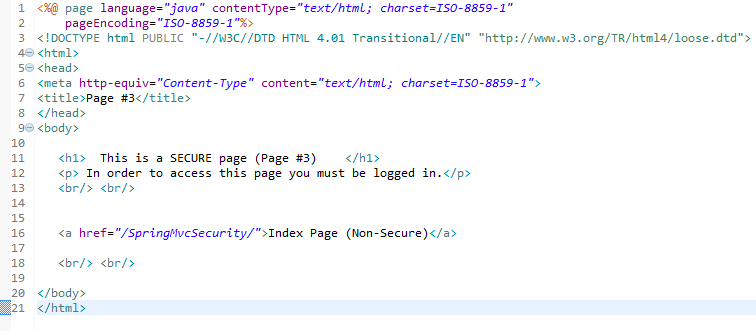
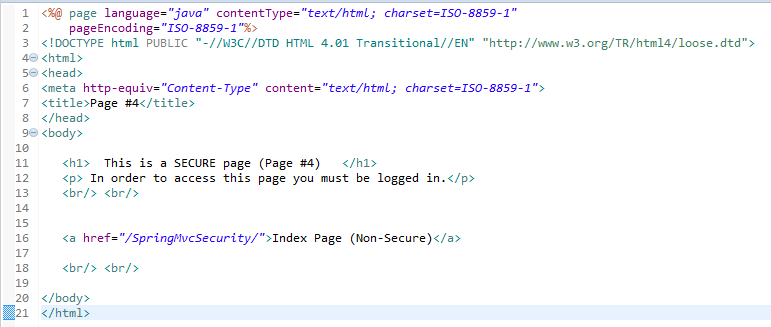
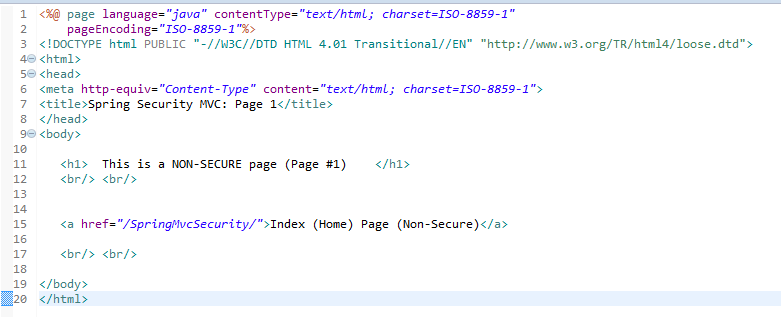
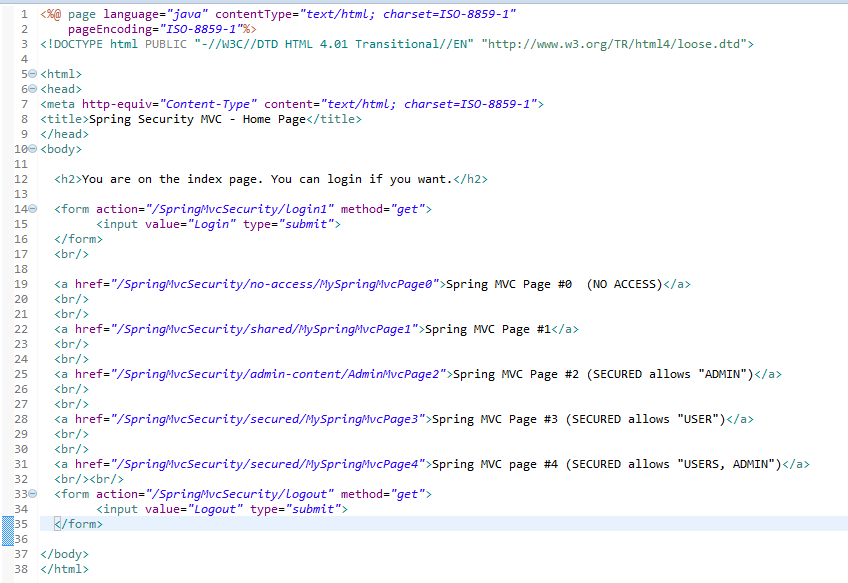
When you run this Spring MVC Application you will see the following screen in the web browser:
Don't click on the Login/Logout buttons yet, but when you click on the links above, you will see that no restriction access is enforced. You can see all the pages. I notice that there is no logging into the application yet. This example shows you an application without security enforcement. You can take a look at the following link in order to see how to enforce MVC application security in Spring 5.

